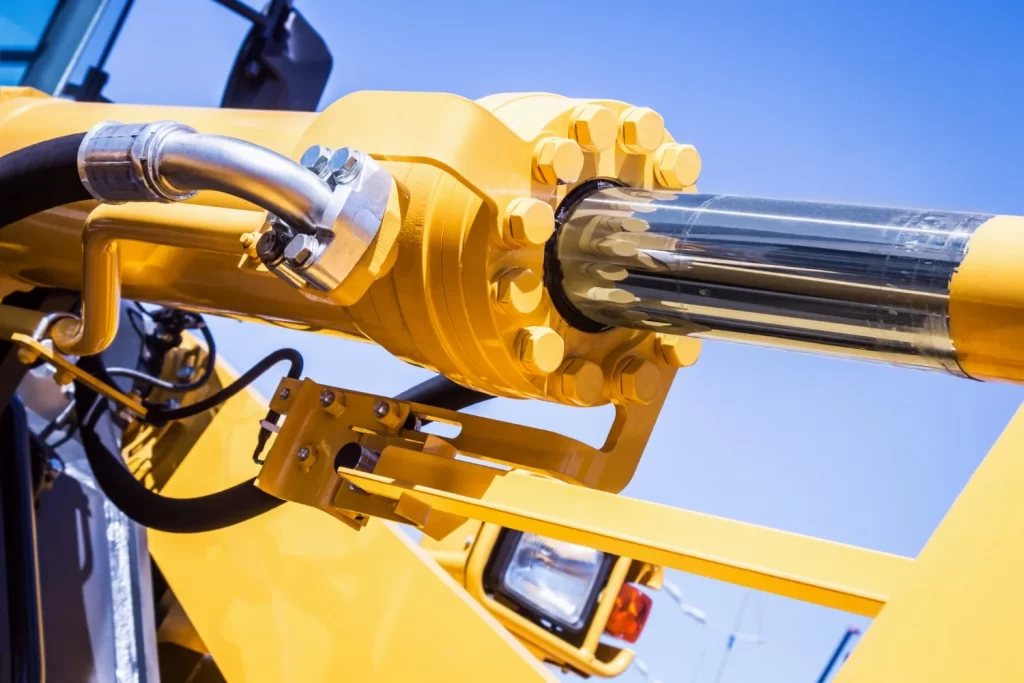
You would have caught a glimpse of heavy machinery lifting an enormous weight with ease or performing very accurate movements with tremendous power. The secret to power and precision is hydraulic cylinders—the backbone of most industrial and mobile devices.
Hydraulic cylinders convert pressurized fluid energy into linear motion under control so that equipment can push, pull, and lift with amazing force. But how is hydraulic cylinder operation achieved?
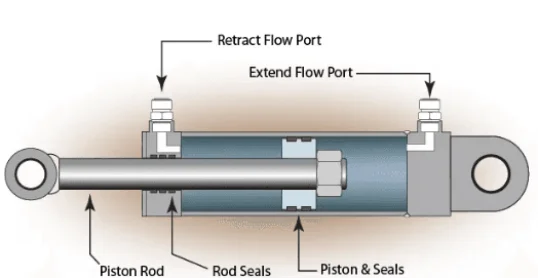
What is a Hydraulic Cylinder’s Unwavering Outer Covering?
The Cylinder Barrel’s Function
Its most externally apparent part is its barrel. At first sight, it may appear to be an ordinary metal pipe, but its function comes before:
- ●Holds the piston and pressurized hydraulic fluid.
- ●Provides structural strength despite high force and motion.
- ●Allows piston smooth movement with an inner honing process.
What Makes the Barrel Durable?
The barrel is usually seamless high-grade steel tubing honed to an extremely smooth internal finish. The process achieves:
- ●Low piston-to-barrel friction.
- ●Minimum fluid leakage for high pressure control.
- ●Better durability to endure years of service.
What Goes Through Inside the Barrel? An Overview of the Piston
How Does the Piston Function
Inside the barrel, the piston is the mechanism which transforms hydraulic pressure into motion. When hydraulic fluid is introduced into the cylinder, it:
Pushes one side of the piston, forcing it.
Convert linear motion along the cylinder’s length.
Seek to transfer power to the piston rod, conveying the external burden through.
For What Purpose Are Seals Fitted on the Piston?
The piston boasts seals, preferably rubber or polyurethane, which:
- Keep the hydraulic fluid away from leakage around pressure zones.
- Initiate smooth effective movement in the barrel.
- Control levels of pressure towards effective functioning.
How is the Power Transferred Out? The Role of the Piston Rod
What is the Role of the Piston Rod?
The piston rod is where internal hydraulic power meets external machinery. It has the following roles:
- Transmit the piston motion to perform work.
- May withstand large forces (tension and compression).
- For constant operation according to accurate manufacturing.
Why is a Piston Rod Long Lasting?
In order to be safeguarded against severe stress and abrasion, piston rods are usually made of cold-rolled steel and hard chrome plating coated, which:
- Resists corrosion and wear on the surface.
- Creates a smooth surface that doesn’t damage the seal.
- Endorses durability and performance under severe conditions.
How is the Cylinder Sealed at Both Ends? An Understanding of the Head and Base
Why is the Cylinder Head?
The cylinder head (or blind end) is located at the opposite end of the piston rod. It acts as:
- A pressure vessel for containing fluid under pressure.
- A support base for seals and ports.
- A structural component to help maintain the strength of the cylinder.
Why is the Cylinder Base (Gland) used?
Located at the very end of the piston rod, the cylinder base (or gland):
- Protects the opening of the piston rod.
- Seals hydraulic fluid leaks.
- Can be a mounting point for the hydraulic system.
The base is typically threaded, bolted, welded, or tied with rod depending on the cylinder type.
What Prevents Leaks and Contamination? The Role of Seals and Glands
What Is the Role of Seals in a Hydraulic Cylinder?
Seals keep the fluid from leaking and contain pressure. Fitted around the cylinder, they are:
- Primary Seals–Keep hydraulic fluid from leaking.
- Secondary Seals–Secondary sealing for added security.
- Wear Bands–Prevent metal-to-metal contact.
- Wipers & Scrapers–Prevent dirt, dust, and contamination.
Why Proper Seal Selection Is Important?
Seal material selection is done correctly on the basis of:
- Cylinder operating pressure and speed.
- Temperature and hydraulic fluid used.
- Environmental exposure (water, chemicals, dust).
Good-quality seals enhance the lifespan of the cylinder and reduce maintenance cost.
How Hydraulic Fluid Enters and Exits: The Function of the Port
What are Hydraulic Cylinder Ports?
Fluid inlets and outlets in and out of hydraulic fluid to:
- Flow into cylinder to build up pressure.
- Exit cylinder when relieving force.
- Regulate motion of the piston by controlled fluid displacement.
Why is Port Design Important?
Ports must be secure and have high-pressure bearing capacity. They are typically:
- Threaded or flanged for close coupling.
- Correctly sized for efficient fluid flow.
- Located strategically based on cylinder design (double-acting or single-acting).
How is the Cylinder Mounted onto Machinery? Knowledge of Mounting Options
Why is Mounting Style Critical?
Mounting options will dictate how a hydraulic cylinder should be mounted into a machine. A well-designed mounting system:
- Provides stability and accuracy.
- Reduces stress against cylinder components.
- Allows for necessary movement in the system.
What are Typical Mounting Techniques?
Different applications require different mounting, such as:
- Clevis Mounts–Permits pivoting motion.
- Flange Mounts–Offers stiff attachment.
- Trunnion Mounts–Permit swinging motion.
- Lug Mounts–Provide fixed, secure attachment.
Why is it Important to Know the Components of Hydraulic Cylinders?
Understanding the functions and interactions of these seven major components is critical to:
- Proper maintenance and repair.
- Successful selection and tailoring of hydraulic cylinders.
- Optimizing efficiency and lifespan of hydraulic equipment.
Looking for Reliable Hydraulic Cylinders? Consider Shining Hydraulics
Shining Hydraulics offers:
- Tailor-made solutions according to your needs.
- Advanced engineering and top-of-the-line manufacturing.
- Tough quality control from raw material choice to end assembly.
Their customer satisfaction and precision engineering focus makes them a worthy partner for hydraulic applications.
Conclusion: The Power Behind Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders are the building blocks of a great deal of equipment essential to operation, converting fluid power into mechanical energy. With their seven primary components, you now understand how they function and how crucial they are for industrial use.
When choosing hydraulic cylinders, quality is the first consideration—providing long life, performance, and reliability over the long term. In maintenance, troubleshooting, or choice, this information places you to make educated choices for optimal performance.