Hydraulic cylinders are of vital use in construction, agricultural, and manufacturing industries. Hydraulic cylinders convert hydraulic fluid pressure to mechanical motion so that machinery is able to perform heavy-duty functions. Any breakage during function in the context of leaks, pressure loss, or abnormal movement shows wear and tear.
It is in such instances that a hydraulic cylinder must be removed for maintenance or replacement of the malfunctioning components. It is in this context that this tutorial gives a step-by-step guide to disassembling a hydraulic cylinder in an effective and safe way.
Learning the Parts of a Hydraulic Cylinder
Learning the basic parts of a hydraulic cylinder is necessary prior to the disassembly.
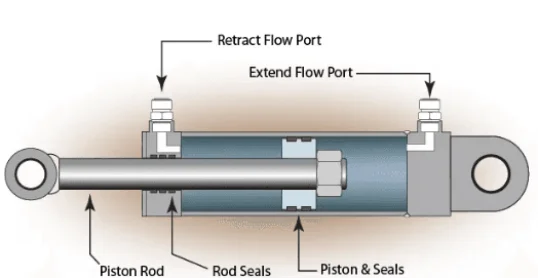
1. Basic Parts of a Hydraulic Cylinder
Cylinder Barrel: Main part with hydraulic fluid and the piston.
Piston and Piston Rod: Piston moves within the barrel, and rod moves and returns to use.
Seals and O-Rings: Keep the leaks from entering and the pressure inside.
End Cap (or Head): Covers one barrel end and prevents fluid leakage.
Gland (or Rod Seal): Covers the piston rod when exiting the cylinder, keeping fluid from leaking out.··
Ports: Vent ports of the cylinder through which hydraulic fluid enters and exits, inducing the movement of the piston.
Proper understanding of these parts is critical to a successful and safe disassembling process.
Safety Precautions Before Disassembling
Disassembling a hydraulic cylinder means working with high-pressure parts, and hence safety precautions are of utmost priority.
1. Safety Procedures as a Requirement
Depressurization of Hydraulic System: Shut down and depressurize the system prior to proceeding.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Prevent accidental start-up through safety procedures.
Cleaning the Cylinder: Clean the cylinder to prevent contamination during disassembly.
Disconnecting Hydraulic Lines: Cap lines when disconnecting to prevent loss of fluid.
Securing the Cylinder: Clamp the cylinder on a workbench or vice to prevent movement.
These procedures reduce risks and enable easy disassembly.
Tools Necessary for Disassembling a Hydraulic Cylinder
Utilizing the right tools makes it easier and prevents damaging parts.
1. Tools Required
Adjustable Spanners and Wrenches: For removal of fasteners and fittings.
Pipe Wrenches: For removal of end caps.
Allen Key Set or Socket Set: Required for fasteners.
Flathead and Phillips Screwdrivers: Helpful in loosening and prying components.
Soft Mallet or Rubber Hammer: For tapping loose components.
Snap Ring Pliers: Required for removal of snap rings.
Spanner Wrench or Pin Spanner: For threaded end caps or glands.
Seal Pick or Small Flat-Head Screwdriver: For prying out seals and O-rings.
Clean Rags and Non-Abrasive Cleaning Solvents: For cleaning components when disassembled.
Safety Equipment: Gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
Having these tools available before beginning ensures smooth work flow.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
1. Preparing the Cylinder for Disassembly
- Ensure the system is depressurized.
- Securely hold the cylinder in position.
- Drain hydraulic fluid by placing a container under the ports and removing the plugs.
- Pull out the piston rod assembly completely if necessary.
2. Retaining Mechanism Removal
- Identify and disconnect the retaining mechanism, such as a wire ring, snap ring, or threaded cap.
- Apply snap ring pliers for snap rings or spanner wrench for threaded caps.
- Use penetrating oil or heat where the mechanism might be frozen.
3. Removing Piston Rod Assembly
- Slowly remove the piston rod assembly directly from the cylinder barrel.
- Don’t rub on cylinder walls to prevent internal damage.
- Use hydraulic pressure or heat only if gland is hard.
4. Removing piston from rod
- The piston is usually locked by a lock nut or by fasteners.
- Don’t loosen fasteners by using a wrench.
- Pull piston off the rod.
- Mark the direction of the piston for assembly.
5. Pulling Seals and Wear Rings
- Remove pull seals and wear rings from cylinder head, gland, and piston with a seal pick cautiously.
- Do not scratch the grooves since damage can make the seal less efficient.
Checking Parts for Damage
Inspect all the parts visually with care after tearing down to ascertain whether replacement is required or not.
1. Key Inspection Areas
Cylinder Bore: Check visually for rust, pitting, and scratches.
Piston Rod: Check for bending, chrome plating damage or scoring.
Piston: Check for crack and seal groove wear.
Seals and O-Rings: Check for wear, deformation, or hardening.
Fasteners and Retaining Rings: Check to confirm that they are not worn or damaged.
Knowledge of the reason for failure avoids repeat failures and improves lifespan.
Reassembling the Hydraulic Cylinder
Reassembly is critical and must be accomplished with meticulous care in cleanliness.
1. Key Reassembly Steps
- Clean parts in advance thoroughly.
- Use fresh hydraulic fluid on new seals and lubricate prior to assembly.
- Assemble piston assembly properly to avoid damage to seals.
- Replace end caps and fasteners and tighten per manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Leak test the cylinder before reinstalling it on machinery.
Preventive Maintenance of Hydraulic Cylinders
Preventive maintenance extends the lifespan of the hydraulic cylinder and reduces failure.
1. Best Maintenance Practices
- Scheduled leakage and wear check.
- Clean the System Regularly: Hydraulic fluid cleanliness and good filtration.
- Replace Seals When Due: Prevents leaks and pressure loss.
- Consult the Manufacturer’s Instruction: Proper use and maintenance.
- Regular servicing ensures better reliability and efficiency.
Professional Service
Disassembling a hydraulic cylinder may be possible on your own, but professional service ensures accuracy and punctuality.
1. Why Shining Hydraulics?
Knowledge and Experience: Over 20 years of hydraulic engineering experience.
Better Manufacture: Enhanced seals and tougher materials.·
Custom Solutions: Hydraulic cylinders for various industries.
Good Performance: Heavy-duty construction with enhanced anti-corrosion processes.
Customer-Centric Approach: Functionality and price as a priority.
Conclusion
Disassembly of hydraulic cylinders must be done with preparation, safety measures, and equipment. Through this step-by-step guide, you can troubleshoot and service your hydraulic cylinders effectively to achieve optimal performance.
But where skill and precision are involved, professional services like Shining Hydraulics provide quality services to keep your equipment in top condition.